
Important Diagrams > Problem solving tips > Mindmap > Cheatsheets.
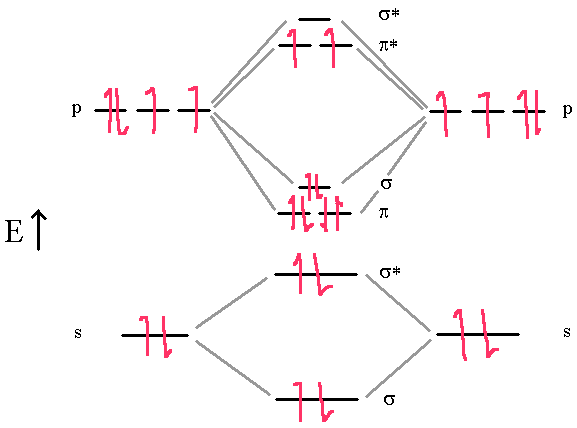
First, though, we need to talk about a new effect, s-p mixing. We will also compare our predictions to experimental evidence. We will predict their bond order and see how the energies of the different orbitals change. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. Join / Login > Class 11 > Chemistry > Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure > Bond Parameters > Calculate the bond. In this section, we will compare MO diagrams for diatomic molecules X-X, from Li 2 to Ne 2. Note: -Electronic configuration of molecular orbital must be according to Hund’s maximum multiplicity rule, according to which the orbital available in the subshell of a molecule are first filled singly with parallel spin electron before they begin to pair and subshell give maximum number of unpaired electron with parallel spin. Click hereto get an answer to your question Calculate the bond order in O2,O2 - ,O22 - and O2 + molecule. Draw the molecular orbital energy diagram for oxygen molecule (O2) and show that: (i) It has a double bond (ii) It has paramagnetic character. Figure 9.7.1: Molecular Orbitals for the H 2 Molecule.
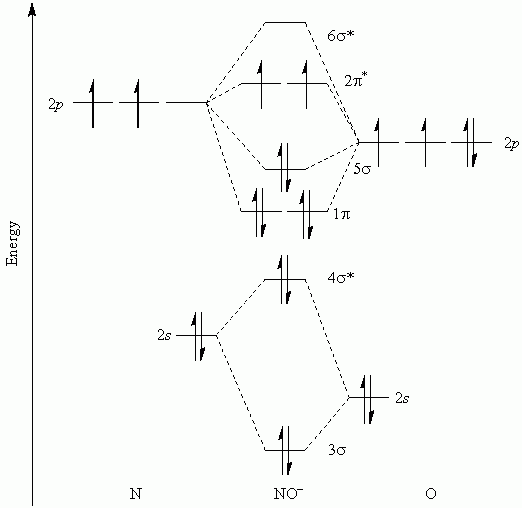
This theory explained the paramagnetic nature of $\text$. Oxygen needs to bond twice, shown as the lone dots on the left and right sides of the oxygen atoms in the below diagram. A molecule must have as many molecular orbitals as there are atomic orbitals. Properties and molecular structure Orbital diagram, after Barrett (2002), showing the participating atomic orbitals from each oxygen atom, the molecular orbitals that result from their overlap, and the aufbau filling of the orbitals with the 12 electrons, 6 from each O atom, beginning from the lowest-energy orbitals, and resulting in covalent.
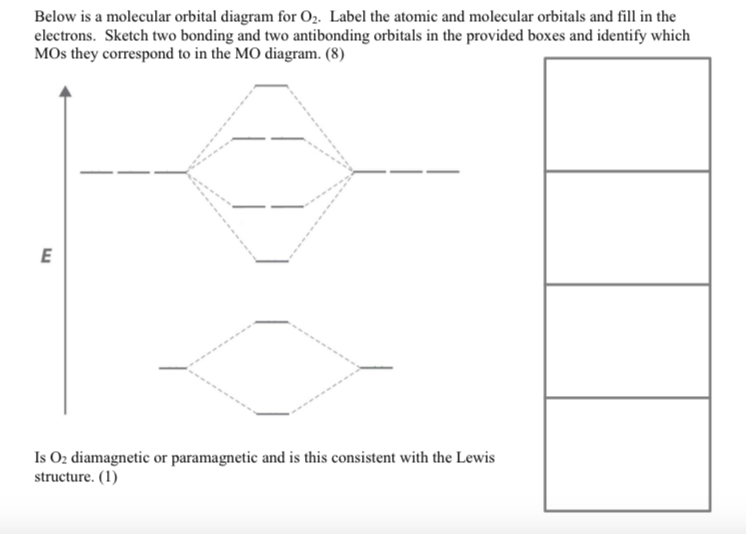
\).Hint: Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and Mulliken, which can be applied to explain the properties, that was not explained by Valence bond theory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
